Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kwon, H.*; Sathiyamoorthi, P.*; Gangaraju, M. K.*; Zargaran, A.*; Wang, J.*; Heo, Y.-U.*; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Lee, B.-J.*; Kim, H. S.*
Acta Materialia, 248, p.118810_1 - 118810_12, 2023/04
被引用回数:15 パーセンタイル:98.95(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Maraging steels, known for ultrahigh strength and good fracture toughness, derive their superior properties from lath martensite structure with high-density nanoprecipitates. In this work, we designed a novel Fe-based medium-entropy alloy with a chemical composition of Fe Co
Co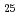 Ni
Ni Mo
Mo in atomic% by utilizing the characteristics of the maraging steels. By a single-step aging of only 10 min at 650
in atomic% by utilizing the characteristics of the maraging steels. By a single-step aging of only 10 min at 650  C, the alloy showed microstructures consisting of a very high number density of (Fe, Co, Ni)
C, the alloy showed microstructures consisting of a very high number density of (Fe, Co, Ni) Mo
Mo -type nanoprecipitates in lath martensite structure and reverted FCC phase, which led to ultrahigh yield strength higher than 2 GPa. This work demonstrates a novel direction to produce strong and ductile materials by expanding the horizons of material design with the aid of high-entropy concept and overcoming the limits of conventional materials.
-type nanoprecipitates in lath martensite structure and reverted FCC phase, which led to ultrahigh yield strength higher than 2 GPa. This work demonstrates a novel direction to produce strong and ductile materials by expanding the horizons of material design with the aid of high-entropy concept and overcoming the limits of conventional materials.
岡 弘; 丹野 敬嗣; 大塚 智史; 矢野 康英; 皆藤 威二
Nuclear Materials and Energy (Internet), 16, p.230 - 237, 2018/08
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:38.11(Nuclear Science & Technology)In determining the nitrogen concentration specifications, nano-structure and high-temperature strength of 9Cr-ODS steel have been investigated as a function of the nitrogen content with the aim of obtaining technical knowledge that makes the specification reasonable. The hardness and tensile strength showed degradation with increasing nitrogen content. For a microstructure, the decrement of residual ferrite phase was confirmed. Since the nitrogen is an austenite stabilizer, the increment of nitrogen enhanced an alpha to  transformation, resulted in the decrease of the residual ferrite phase. It is considered that the reduction of the strength is due to the decrease of the residual ferrite phase.
transformation, resulted in the decrease of the residual ferrite phase. It is considered that the reduction of the strength is due to the decrease of the residual ferrite phase.
石原 正博; 柴田 大受; 馬場 信一; 星屋 泰二; Wan, C.*; 本橋 嘉信*
Proceedings of OECD/NEA 2nd Information Exchange Meeting on Basic Studies in the Field of High-temperature Engineering, p.113 - 124, 2001/00
高温工学に関する先端的基礎研究として大学との共同研究として進めている超塑性セラミックスに関するHTTRを用いた高温照射試験の現状について、超塑性ジルコニアセラミックスの炉外試験の結果を中心に、以下の2つについてまとめたものである。(1)超塑性変形の与える熱物性への影響,(2)超塑性変形の与える機械力学的物性への影響。熱物性への影響では、超塑性変形後の比熱の変化について得られた実測データから、約5%程度の変形では影響が表れないことを示した。また、機械力学的物性への影響では微小硬さ計を用いたダイナミック硬さ及びヤング率測定結果が、超塑性変形による結晶粒の成長や変形による相変化の影響を受けることを述べた。
 -like diffraction anomaly in the premartensitic
-like diffraction anomaly in the premartensitic 
 phase of AuCuZn
phase of AuCuZn alloy
alloy永澤 耿*; 喜田 和枝*; 森井 幸生; 渕崎 員弘; 片野 進; 舩橋 達; H.R.Child*
Mater. Trans. JIM, 32(11), p.1011 - 1016, 1991/00
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:47.83(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Heusler型結晶構造をもつ
 相AuCuZn
相AuCuZn 合金について(H
合金について(H 2/3,K
2/3,K 2/3,L
2/3,L 4/3)と(H
4/3)と(H 2/3,K
2/3,K 2/3,L
2/3,L 4/3)の逆格子点にあわられる
4/3)の逆格子点にあわられる ピーク状の回折ピークをX線と中性子を用いて調べた。このピークは不完全規則B
ピーク状の回折ピークをX線と中性子を用いて調べた。このピークは不完全規則B 相において、670KでHensler型規則構造へと変態する際の規則化を担う空孔が、ある種の規則配列をしたために起こることが判明した。この空孔は急冷処理によってHeusler型構造の中に凍結されると、
相において、670KでHensler型規則構造へと変態する際の規則化を担う空孔が、ある種の規則配列をしたために起こることが判明した。この空孔は急冷処理によってHeusler型構造の中に凍結されると、 ピーク状回折異常をもたらし、その後の昇温により空孔がなくなると、回折異常も消滅する。[111]LA、[112]TAフォノン分散関係の特徴も以上の結論を支持している。
ピーク状回折異常をもたらし、その後の昇温により空孔がなくなると、回折異常も消滅する。[111]LA、[112]TAフォノン分散関係の特徴も以上の結論を支持している。
石塚 雅之*; 佐藤 次男*; 遠藤 忠*; 島田 昌彦*; 大野 英雄; 井川 直樹; 長崎 正雅
Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 73(8), p.2523 - 2525, 1990/00
被引用回数:13 パーセンタイル:55.13(Materials Science, Ceramics)Y O
O を添加して作製した正方晶ジルコニア多結晶体(Y-TZP)は高強度・高靱性を有する材料であり、耐熱性構造材料としての利用に期待されている。耐熱性構造材料として利用する場合、高い熱衝撃抵抗を有することが望ましいが、Y-TZPにおけるその値は熱膨張係数、ヤング率、熱伝導度等の物理的性質から予想される値に比べ著しく小さく、その改善が望まれる。本論文は、こうしたY-TZPに関して、熱応力によって引き起こされた微小亀裂付近の相変態挙動をレーザーラマン分光光度計を用いて分析し、粒子径変化に対する熱衝撃破壊挙動の観点から解析を行なったものである。その結果として、Y-TZPの粒子径が大きくなるに従って、微小亀裂付近の応力誘起相変態量が増加し、従って、熱衝撃抵抗が向上することを見出した。
を添加して作製した正方晶ジルコニア多結晶体(Y-TZP)は高強度・高靱性を有する材料であり、耐熱性構造材料としての利用に期待されている。耐熱性構造材料として利用する場合、高い熱衝撃抵抗を有することが望ましいが、Y-TZPにおけるその値は熱膨張係数、ヤング率、熱伝導度等の物理的性質から予想される値に比べ著しく小さく、その改善が望まれる。本論文は、こうしたY-TZPに関して、熱応力によって引き起こされた微小亀裂付近の相変態挙動をレーザーラマン分光光度計を用いて分析し、粒子径変化に対する熱衝撃破壊挙動の観点から解析を行なったものである。その結果として、Y-TZPの粒子径が大きくなるに従って、微小亀裂付近の応力誘起相変態量が増加し、従って、熱衝撃抵抗が向上することを見出した。
諸岡 聡; 井川 直樹; 佐々木 未来; 生田目 望; 樹神 克明
no journal, ,
Medium Mn steels have been actively investigated due to their excellent balance between material cost and mechanical properties. In particular, medium Mn steel with a nominal chemical composition of Fe-5.0Mn-0.1C (mass%) fabricated by intercritical annealing 923 K for 1.8 ks after cold-rolling, was the high-strength mechanical properties at low temperature. This strengthening mechanism evaluated by means of in-situ neutron diffraction under low temperature (High Resolution Powder Diffractometer (HRPD) at Japan Research Reactor-3(JRR-3)), electron back scatter diffraction (EBSD), low temperature differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and low temperature magnetic susceptibility measurement. We found that as the sample temperature decreases, face- centered cubic (FCC) structure transferred face-centered tetragonal (FCT) structure. Namely, it suggests that austenite transformed martensite like Fe-Pd or Fe-Pt alloy. Therefore, the origin of the high-strength mechanical properties at low temperature was in the presence of FCT martensite.
諸岡 聡; 小山 元道*; 川崎 卓郎; Harjo, S.
no journal, ,
Medium Mn steels have been actively investigated due to their excellent balance between material cost and mechanical properties. In particular, medium Mn steel with a nominal chemical composition of Fe-5.0Mn-0.1C (mass%) fabricated by intercritical annealing 923 K for 1.8 ks after cold-rolling, was the high-strength mechanical properties at low temperature. This strengthening mechanism evaluated by means of in-situ neutron diffraction under low temperature (engineering materials diffractometer (TAKUMI) at Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC)), electron back scatter diffraction (EBSD), low temperature differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and low temperature magnetic susceptibility measurement. We found that as the sample temperature decreases, face-centered cubic (FCC) structure transferred face-centered tetragonal (FCT) structure. Namely, it suggests that austenite transformed martensite like Fe-Pd or Fe-Pt alloy. Therefore, the origin of the high-strength mechanical properties at low temperature was in the presence of FCT martensite. This study got partially support from MEXT Program: Data Creation and Utilization Type Material Research and Development (JPMXP1122684766).